PET vs PETG, this material is pretty much everywhere in our daily lives. The most important reason being its low cost and ease of availability of the material.
While you’re aware that bottles, packaging materials, automotive parts, fabric industry and electrical parts mostly use PET. On the other hand PETG is widely used as a robust alternative for mechanical parts and mid temperature resistance behavior.
As a demand from 3D printing enthusiast like us, PET material is commonly available as a filament.
In this article, from a perspective of a 3D Printing enthusiast / professional, we will understand the following as below….
- Deeply analyze the major differences in PET vs PETG material.
- Material properties
- What is the G factor
- Printing settings
- When should you choose PETG
- Pros & Cons
- Practical Experiences
- Conclusion
Continue reading to understand key differences between PET vs PETG and identify the practical applications in your projects.

The G- Factor
From the basics, Lets look at the chemical structure of PET and PETG
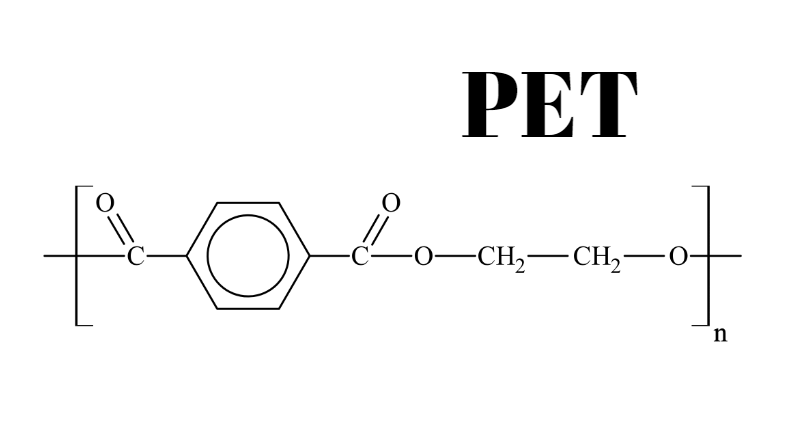
Generally, there is a common misunderstanding that the PETG is formed by adding G – Glycol additive to PET. Lets understand the basics of PETG which will help us to determine our applications
PETG – ‘Glycol-G’
To understand the chemistry that matters in our perspective, Glycol is generally a chemical structure that contains oxygen and hydrogen (-OH) at both the ends. In this way there might be many other chemical structures that can be considered glycols. However in our case, this is not the same in PET vs PETG
The glycol added makes it more hazy and reduces the brittleness. This is an important material property to overcome cons of PET.
Chemical Process of PET & PETG
In the preparation of PET (Polyethylene terephthalate) typically its formed by combining dimethyl terephthalate and ethylene glycol. These are the building blocks of PET polyester.
However in the preparation of PETG, a different type of glycol monomer is added, which is Cyclohexanedimethanol. So now that we know the chemical differences between these two polyesters, lets analyse the major material properties and its differences.
Major Differences between PET & PETG
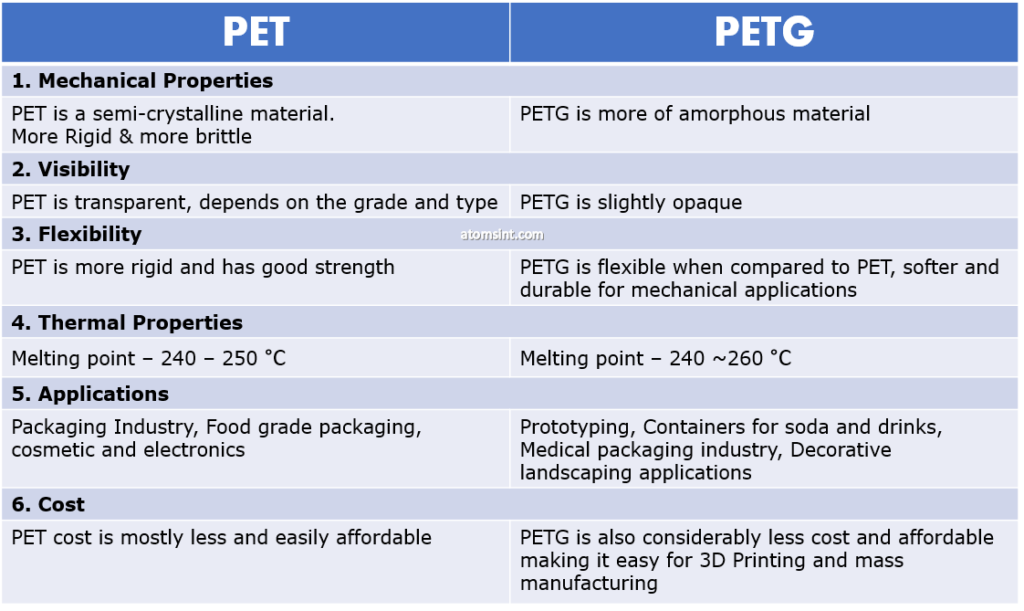
The primary difference in terms of material property of these two materials is that, PET is kind of stiff material and PETG is slightly flexible. PET is slightly on the brittle side, whereas the PETG has more impact resistance
PET absorbs more moisture compared to PETG. Its always advised to store the PET filament in dry environment. If it tends to get wet, you can use a dryer to remove moisture.
When should you choose PETG?
PETG has high impact resistance than the PET, thus making it more harder. PET is more brittle and more rigid and this properties can be applied to a selective parts. However, PETG can be applied for many parts.
It has a good finish quality and hence can be used in the final display products for much better aesthetic appearance. PETG was widely used in the COVID pandemic period as face shields. Thus PETG finds itself in various industry applications such as medical implants. Due to its non-hydroscopic nature PETG can be easily used for cosmetic applications and food grade applications.
Less shrink-ability enhances its applications for large prints and ideal for softer and flexible parts. Unlike PET, this has no odor. Due to its softer nature, its widely used in food packaging and flexible brackets for mechanical applications. PETG has better load resistance such as ABS.
Hence PETG has more better advantages over PET from a 3D Printing perspective. Due to its good chemical resistance behavior its widely used in food packaging industry and making it perfect for optimizing weight.
What is PETG best for?
PETG is well known for its high impact resistance, flexibility, low hygroscopic, High temperature resistance, Better color absorption, chemical resistance, thus making it a better candidate for high stress environment and durable for a long periods of time.
Pros & Cons of PET
| PROS | CONS |
|---|---|
| Easy recyclable | Non Biodegrade |
| Better Strength to weight ratio | PET is prone to oxidation |
| Affordable and ease of availability | Low heat resistance |
| Food grade and transparent | Crude oil byproduct |
Printable Settings:
These are the below printable settings suitable for PET & PETG. Based on the machine maker, filament and the practicality of the part, these are subject to be customized.
Basic Print settings for PETG:
Nozzle temperature: 235°C~260°C
Bed Temperature: 55°C~70°C
Printing speed: 45~56 mm/s
Retraction : 0.8~1.3mm
Remember that the print settings are subjected to change according to the part geometry and infills settings, based on the initial print impressions, you can slightly modify the print settings.
Practical Experiences in 3d Printing PETG
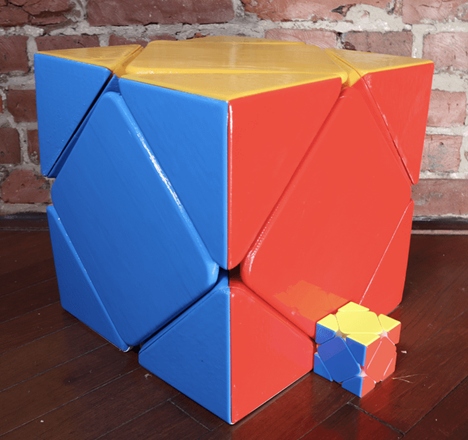
Below is the biggest print possible by PETG material, thanks to its low shrinkage and excellent color absorption property
The below image shows the PETG print for the first time and we can clearly see the tiny artifacts, this might due to the flow rate in the nozzle. Try to increase it and better to use non-sticky type nozzle such as nickel plated which will try to reduce such quality issues in 3D printing PETG.

Conclusion: PET vs PETG
Lets wrap this up, after considering the above points and material properties, PETG and PET having the same printing temperature. However, based on the nature of your part, application and design features the desired material should be selected.
PET and PETG have different properties, if you’re looking for the durable and high impact resistance then PETG is the right fit. PET has better tensile strength and excellent recyclability. PETG has best chemical resistance and mechanical properties making it right material for food grade and flexible shields.
To conclude. from the 3d printing perspective, PETG is more advantageous to PET, however it depends on the nature of the part.
Did you like the above comparison. Which one would you try it? Please do let us know in the comment section below.
Looking for a slicer difference cura vs creality? Please read it here to know more.
