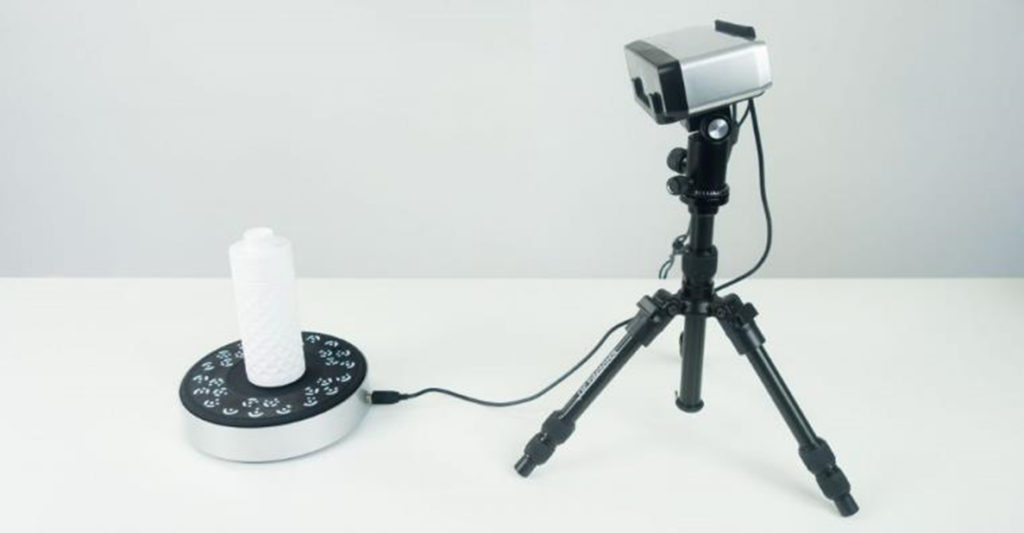
A line of laser light is used in 3D laser scanning, a non-contact, non-destructive technology, to digitally capture the shape of real-world items. “Point clouds” of data are produced from an object’s surface by 3D laser scanners. In other words, 3D laser scanning is a technique for accurately transferring the size, shape, and dimensions of a physical thing into a digital, three-dimensional representation.
In order to swiftly produce point clouds with a high degree of accuracy, 3D laser scanners measure minute details and record free-form shapes. When measuring and inspecting curved surfaces and complex geometries that require enormous amounts of data for an accurate description and when doing so is impractical with the use of a touch probe, 3D laser scanning is the best option.

The 3D Scanning Process:
3D laser scanning is used for data acquisition
Process of 3D laser scanning The digitizer’s bed is used to place the object to be laser scanned. The laser probe is raised above the surface of the item by specialized software. Two sensor cameras constantly capture the shifting length and shape of the laser line in three dimensions (XYZ) as it sweeps along the surface of the item while the laser probe projects a line of laser light onto the surface
Resulting Data
As the laser goes around, capturing the full surface contour of the object, a “point cloud” representing the shape of the object is displayed on the computer screen. Up to 750,000 points can be collected per second, and the technique is quite accurate (to.0005′′).
Modeling Choice Depends on Application
The massive point cloud data files are produced, registered, and combined into a single three-dimensional representation of the object before being post-processed using different software programs appropriate for a certain application.
Point Cloud Data for Inspection
The scanned object can be compared to the designer’s CAD nominal data if the data is to be used for inspection. A “color map deviation report” in PDF format, which visually illustrates the variations between the scan data and the CAD, is the end result of this comparison process.data.CAD Model for Reverse Engineering
The quickest, most precise, most automated method of obtaining 3D digital data for reverse engineering is by laser scanning. Once more, specialist software is utilized to construct a 3D CAD model of the geometry of the part using the point cloud data. The CAD model allows for the accurate reproduction of the scanned object or for the modification of the object to rectify flaws. Depending on the need, Laser Design can produce a surface model or a more complicated solid model.